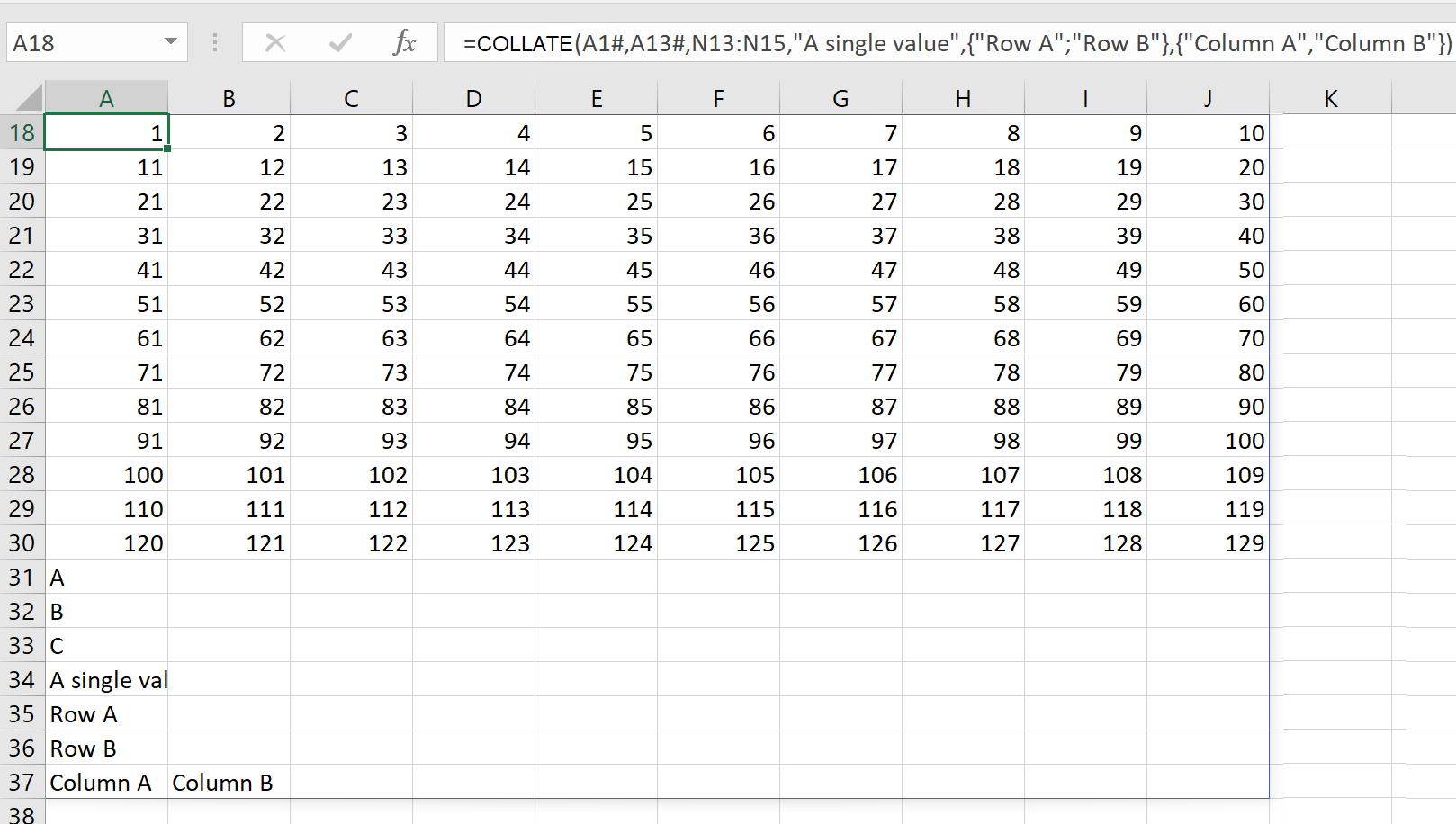
Description
The COLLATE function combines multiple arrays or ranges into a single array.
Velixo recommends the use of Microsoft 365 for this feature. Experimentally, Excel 2010 or higher may be used. See the Prerequisites for additional information.
Overview
The COLLATE function supports any valid Excel reference. Including:
-
An Excel 365 spill range (ex: A1#)
-
A standard range (ex: N13:N15)
-
An individual cell (ex: N15)
-
A direct value (ex: "Hello")
-
An inline array of rows or columns:
-
Rows are separated by semicolons: {"Row A" ; "Row B"}
-
Columns are separated by commas: {"Column A" , "Column B"}
-
The arrays and ranges do not have to contain the same number of columns; the resulting array will be as wide as the widest range passed to COLLATE()
Syntax
=COLLATE(
Array [or range],
Array [or range]
)
Arguments
The COLLATE function uses the following argument:
|
Argument |
Required/Optional |
Description |
|
|
Required |
The arrays and/or ranges to be combined |
By nature, the function uses multiple arrays and/or ranges)
Examples
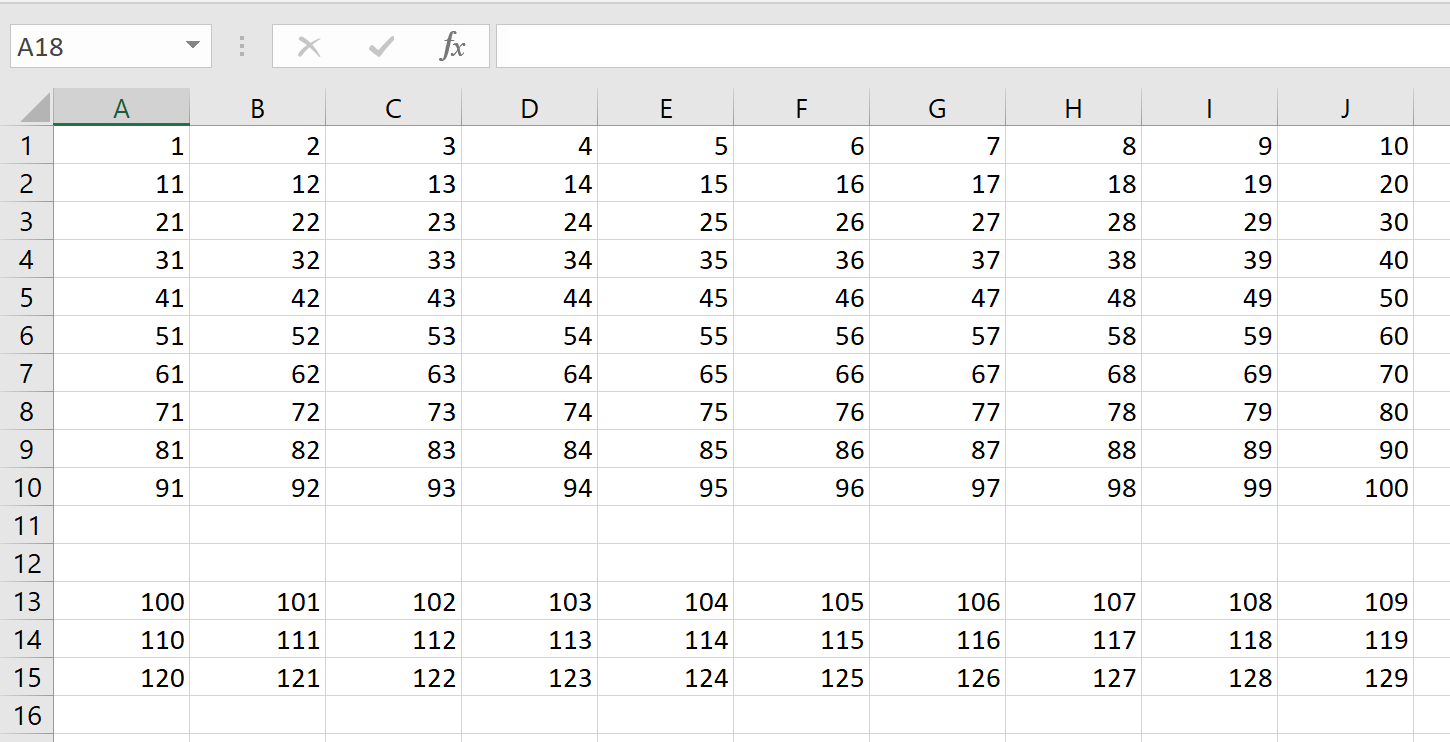
Example 1
Let us consider an Excel 365 worksheet with two arrays (one defined in cell A1, the other defined in cell A13):
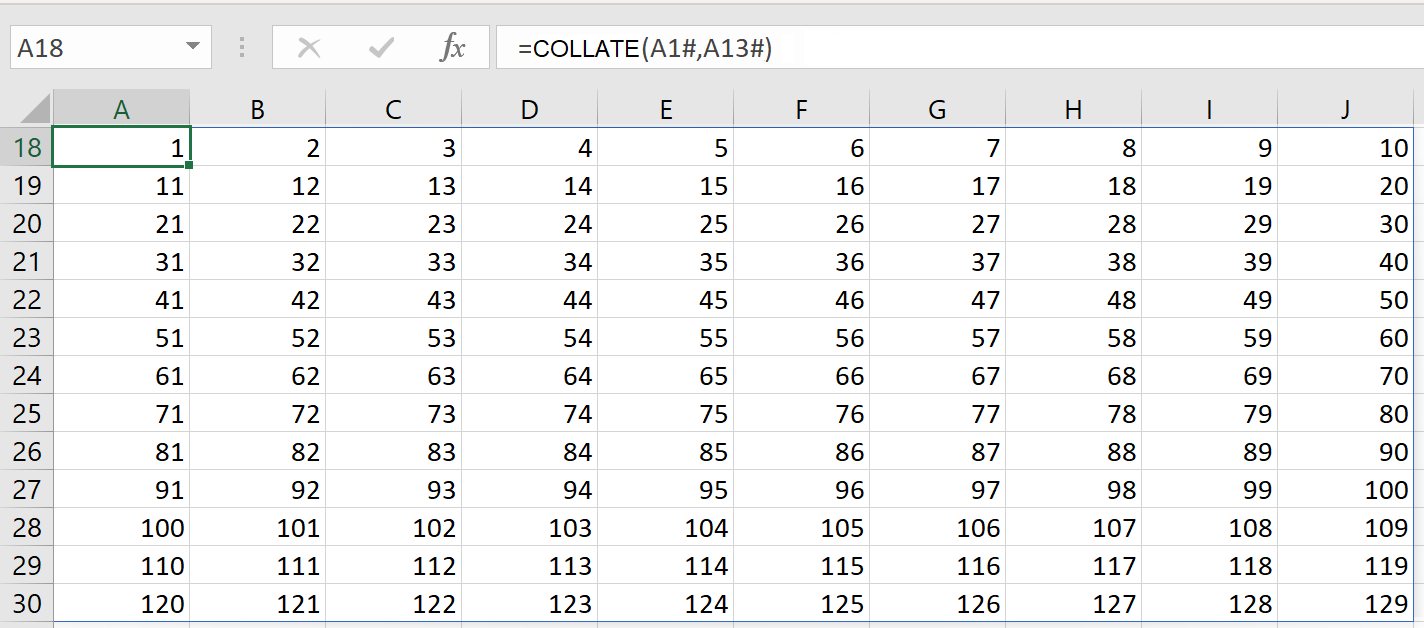
Using the COLLATE function...
=COLLATE(
A1#,
A13
)
...we can combine them into one array:
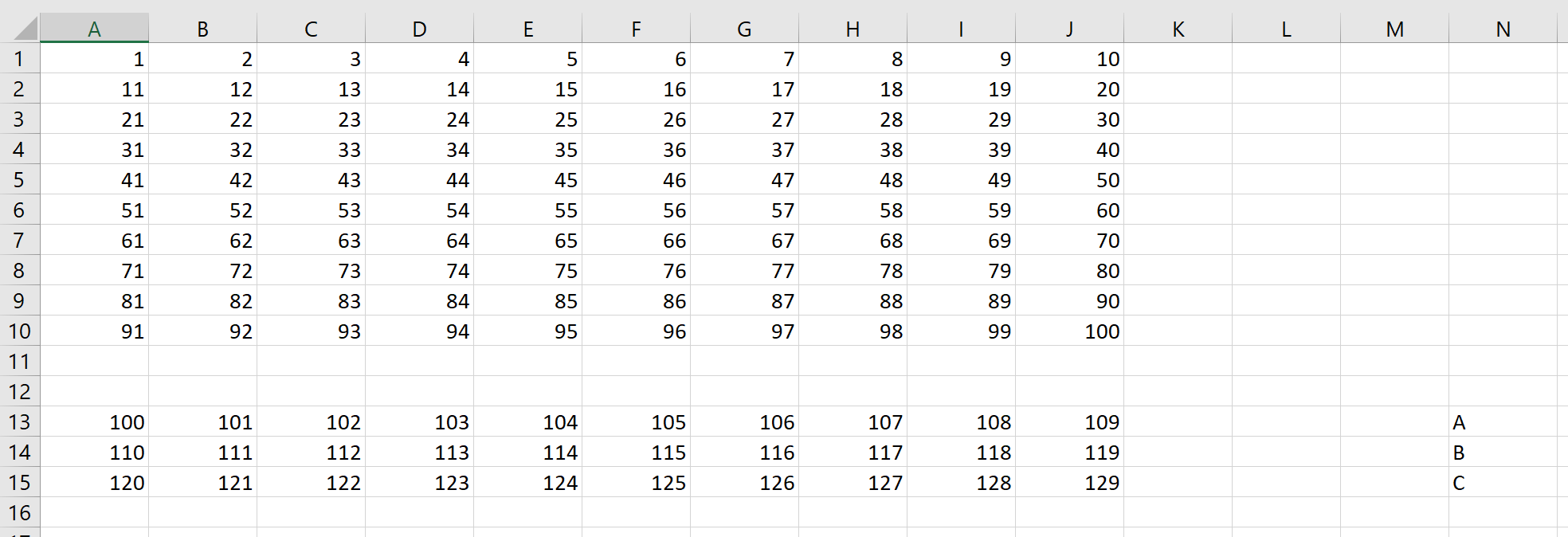
Example 2
Given those same arrays, plus some additional data in column N:
Using the COLLATE function, we can combine all of those, plus additional data:
=COLLATE(
A1#,
A13,
N13:N15,
"A single value",
{"Row A"; "Row B"},
{"Column A", "Column B"}
)